Today, we will delve into the fascinating and often mysterious world of the creative process. From the initial spark of an idea to its final execution, we will explore each step along the way, uncovering the secrets that can unlock your own creative potential. Whether you are a writer, artist, entrepreneur, or simply someone looking to add a touch of creativity to your everyday life, understanding the creative process can be a powerful tool. So, prepare to dive into the realm of inspiration and innovation as we unveil the path from idea generation to execution.
This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
The Creative Process Unveiled
From Idea Generation to Execution
Creativity is a fundamental aspect of the human experience. It is the force that drives innovation, problem-solving, and self-expression. But what exactly is creativity? And why is it so important in our lives? In this article, we will explore the various stages of the creative process, from idea generation to execution, and uncover the myths surrounding creativity. By understanding and embracing the creative process, you can tap into your full potential and unleash your creative genius.
1. Understanding Creativity
1.1 Defining Creativity
Creativity can be defined as the ability to generate unique ideas, solutions, or expressions that are valuable and original. It involves breaking free from conventional thinking and embracing a mindset that encourages innovation and experimentation. Creativity encompasses a wide range of domains, including art, science, literature, business, and everyday life.
1.2 The Importance of Creativity
Creativity is crucial in both personal and professional settings. It allows us to approach problems from new perspectives, come up with innovative solutions, and adapt to changing circumstances. In the workplace, creativity fosters a culture of innovation, enhances productivity, and promotes a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction. On a personal level, creativity brings joy, self-expression, and personal growth.
1.3 Myths about Creativity
There are several myths surrounding creativity that often hinder our ability to tap into our creative potential. One common myth is that creativity is a gift that only a select few possess. In reality, creativity is a skill that can be developed and nurtured through practice and exploration. Another myth is that creativity is a random and spontaneous process. While inspiration can strike unexpectedly, creativity requires discipline, focus, and a systematic approach.
This image is property of ideapod.com.
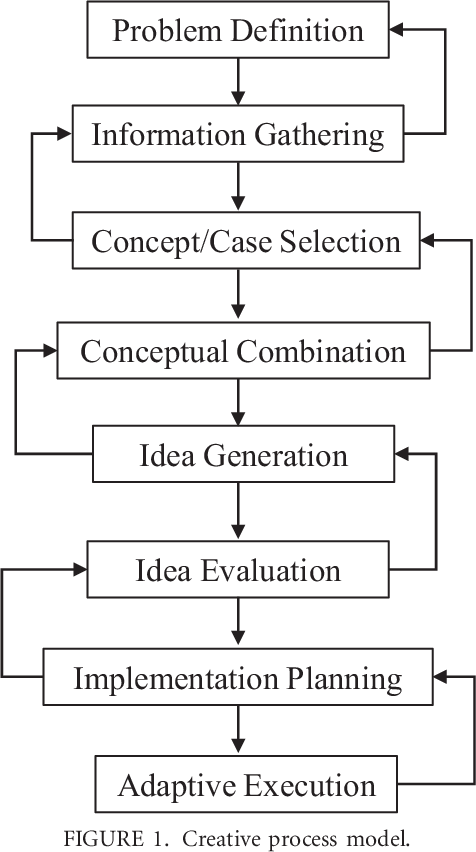
2. The Stages of the Creative Process
2.1 Inspiration and Idea Generation
The creative process begins with inspiration and idea generation. This is the stage where you gather raw materials, explore different perspectives, and generate a pool of ideas. Sources of inspiration can come from various places, such as nature, art, books, conversations, or personal experiences. Techniques for idea generation include brainstorming, mind mapping, free writing, and visualizing.
2.2 Research and Information Gathering
Once you have a pool of ideas, it’s time to delve deeper and gather relevant information. This stage involves conducting thorough research, defining your goals and objectives, and exploring different perspectives and possibilities. Research can involve reading books, articles, and studies, conducting interviews, or exploring online resources. The goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the topic at hand and explore different angles and possibilities.
2.3 Incubation and Reflection
After gathering information, it’s important to give your ideas time to incubate and reflect. This stage involves stepping away from the problem and allowing your subconscious mind to process the information. Take breaks, engage in activities that inspire you, and create space for reflection. During incubation, ideas may spontaneously emerge, connecting seemingly unrelated concepts and generating new insights.
2.4 Evaluation and Selection
Once your ideas have had time to incubate, it’s time to evaluate and select the most promising ones. This stage involves analyzing and assessing each idea based on a set of predefined criteria. Consider factors such as feasibility, relevancy, originality, and potential impact. By carefully evaluating your ideas, you can identify the ones with the most potential for further development.
2.5 Planning and Organization
After selecting your ideas, it’s time to move into the planning and organization stage. This involves setting clear goals and objectives, creating a project plan, and defining tasks and deadlines. Break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks, and allocate resources such as time, budget, and manpower. A well-structured plan will provide a roadmap for the execution phase and ensure a smooth workflow.
2.6 Execution and Implementation
With a solid plan in place, it’s time to take action and bring your ideas to life. This stage involves executing the tasks outlined in the project plan, using the available resources effectively, and staying focused and disciplined. It’s important to overcome challenges and obstacles that may arise during the execution phase and adapt as needed. Collaboration with others can also enhance the creative process by bringing fresh perspectives and skills to the table.
2.7 Reflection and Iteration
After executing your ideas, it’s important to reflect on the process and outcomes. This stage involves evaluating the success of your project, identifying areas for improvement, and learning from both your successes and failures. Reflection allows you to refine your ideas, iterate on your approach, and continuously improve your creative process. It is a crucial step in nurturing your creativity and growing as a creative individual.
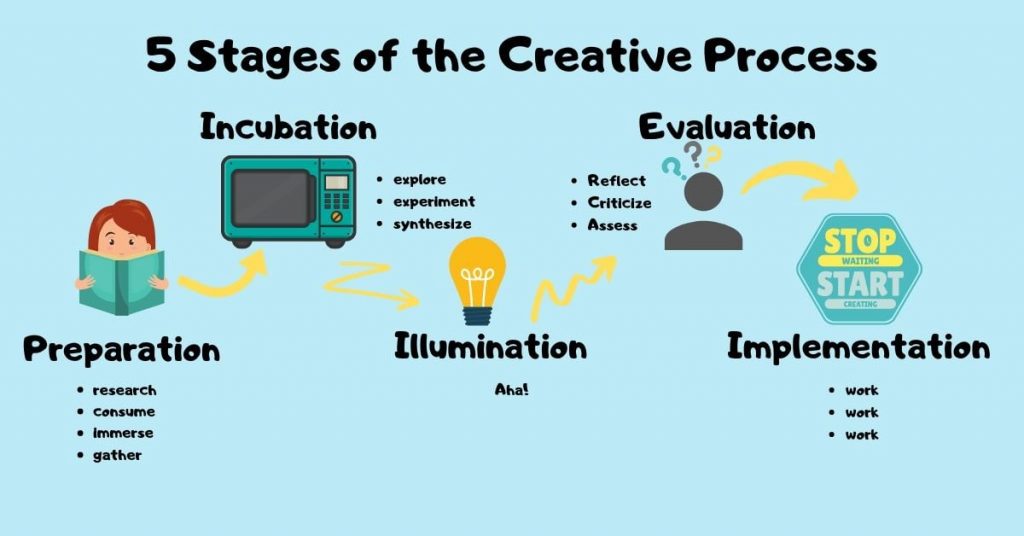
3. Stage 1: Inspiration and Idea Generation
3.1 Sources of Inspiration
Inspiration can be found in a multitude of places. It can come from observing the beauty of nature, engaging in stimulating conversations with others, or immersing yourself in various forms of art and literature. Pay attention to the world around you and be open to new experiences. Inspiration can often be found in the most unexpected places.
3.2 Techniques for Idea Generation
There are numerous techniques you can use to generate ideas. Brainstorming, for example, involves freely generating as many ideas as possible without judgment or evaluation. Mind mapping is another effective technique that allows you to visually organize your thoughts and ideas. Free writing involves continuously writing for a set period of time without worrying about grammar or coherence. Experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you.
3.3 Overcoming Creative Blocks
Creative blocks are inevitable and can be frustrating. When faced with a creative block, it’s important to approach it with patience and curiosity. Engage in activities that inspire you, take breaks to clear your mind, and seek inspiration from others. Sometimes, simply taking a step back and allowing the ideas to incubate can help overcome creative blocks. Most importantly, don’t be too hard on yourself. Creativity is a journey, and setbacks are a natural part of the process.

This image is property of Amazon.com.
4. Stage 2: Research and Information Gathering
4.1 Defining Your Goals and Objectives
Before diving into research, it’s important to define your goals and objectives. What do you hope to achieve with your creative endeavor? What specific questions do you want to answer? Defining your goals will provide clarity and focus during the research process, ensuring that you gather relevant and valuable information.
4.2 Conducting Thorough Research
Thorough research is essential for gaining a deep understanding of the topic at hand. This involves exploring various sources of information, such as books, articles, studies, and online resources. Take notes, highlight key points, and record any insights that emerge during your research. Don’t be afraid to dig deep and explore different perspectives and viewpoints.
4.3 Gathering Relevant Information
As you conduct your research, focus on gathering information that is directly relevant to your goals and objectives. Filter out any irrelevant or unnecessary information to avoid getting overwhelmed. Organize your findings in a way that makes sense to you, whether it’s through digital tools, physical folders, or mind maps. Having a well-organized information repository will make it easier to synthesize and utilize the collected data later on.
4.4 Synthesizing and Organizing Information
Once you have gathered the relevant information, it’s time to synthesize and organize it. Look for patterns, connections, and insights that emerge from your research. Create an outline or a framework that organizes the information in a logical and coherent manner. This will serve as a foundation for the next stages of the creative process.
5. Stage 3: Incubation and Reflection
5.1 Allowing Ideas to Mature
After gathering information, it’s important to give your ideas time to incubate and mature. This involves stepping away from the problem and engaging in activities that inspire you or bring you joy. Allow your subconscious mind to process the information and make connections on its own. Often, the best ideas emerge when we least expect them.
5.2 Creating Space for Reflection
Reflection is a key aspect of the creative process. Create space in your daily life dedicated to quiet reflection and introspection. This could be through practices such as meditation, journaling, or simply going for a walk in nature. Engaging in these practices allows you to gain clarity, connect with your inner self, and tap into your intuition and creative insights.
5.3 Unconscious Processing
Our brains continue to work on problems even when we are not consciously thinking about them. This unconscious processing is an essential part of the creative process. Sometimes, taking a break from actively thinking about a problem can lead to sudden insights and solutions. Trust your subconscious mind and give it the time and space it needs to work its magic.
5.4 Seeking Inspiration from Others
Seeking inspiration from others is a valuable practice in nurturing your creative mindset. Engage with other creative individuals, whether it’s through conversations, attending workshops or conferences, or consuming their work. Allow their ideas and perspectives to inspire and challenge you. Collaboration and sharing ideas can lead to unique insights and fuel your creativity.

This image is property of alumni.sae.edu.
6. Stage 4: Evaluation and Selection
6.1 Criteria for Evaluation
When evaluating your ideas, it’s important to establish a set of criteria to guide your assessment. Consider factors such as feasibility, relevancy, originality, potential impact, and alignment with your goals and objectives. Prioritize ideas that align with your vision and have the potential to make a meaningful contribution.
6.2 Analyzing and Assessing Ideas
Analyze and assess each idea based on your predefined criteria. Break down each idea into its components and evaluate its merits. Consider potential obstacles, risks, and the resources required for implementation. This analysis will help you make informed decisions and choose the ideas with the highest potential for success.
6.3 Selecting the Most Promising Ideas
After careful evaluation and analysis, select the ideas that show the most promise for further development. These are the ideas that align with your goals, have the potential for impact, and are feasible given your available resources. Remember, not all ideas will make the final cut, and that’s okay. Prioritize quality over quantity, and choose the ideas that truly resonate with you and have the potential to create the desired outcome.
7. Stage 5: Planning and Organization
7.1 Setting Goals and Objectives
In the planning and organization stage, it’s important to set clear goals and objectives for your creative project. What do you hope to achieve? What steps do you need to take to get there? Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals will provide a roadmap for your creative journey and ensure clarity and focus.
7.2 Creating a Project Plan
Create a project plan that outlines the steps, tasks, and milestones required to achieve your goals. Break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks and assign deadlines to each task. Consider dependencies, risks, and potential obstacles, and create contingency plans accordingly. A well-structured project plan will provide guidance and help you stay organized and on track.
7.3 Defining Tasks and Deadlines
Define specific tasks that need to be completed for each milestone and assign deadlines to ensure progress and accountability. Break down tasks into smaller subtasks, if necessary, to make them more manageable. Consider your available resources, such as time, budget, and manpower, when assigning tasks and deadlines. Keep your plan flexible and be prepared to adjust as needed.
7.4 Allocating Resources
Allocate the necessary resources to support the execution of your creative project. This includes assigning human resources, securing funding or budget, and identifying the tools and materials required. Consider any constraints or limitations that may impact resource allocation, and find creative solutions to make the most of the resources available to you.
This image is property of fourweekmba.com.
8. Stage 6: Execution and Implementation
8.1 Taking Action on the Plan
With a solid plan in place, it’s time to take action and implement your ideas. Start working on the tasks outlined in your project plan, keeping in mind the specific deadlines and milestones. Break large tasks into smaller, manageable steps to maintain momentum and to prevent overwhelm. Consistency and perseverance are key during the execution phase.
8.2 Overcoming Challenges and Obstacles
Challenges and obstacles are inevitable during the creative process. It’s important to anticipate and prepare for potential roadblocks, and to develop strategies to overcome them. Stay adaptable and flexible, and be open to adjusting your plan as new information or challenges arise. Seek support and guidance from others, and don’t be afraid to ask for help when needed.
8.3 Collaborating with Others
Collaboration can greatly enhance the creative process. Engage with others who have complementary skills and perspectives, and leverage their expertise to bring your ideas to life. Collaborative projects often lead to innovative solutions and unexpected insights. Foster a culture of open communication, trust, and mutual respect to create a supportive and collaborative environment.
8.4 Adjusting and Adapting as Needed
Throughout the execution phase, regularly assess your progress and adjust your plan as needed. Recognize that creativity is a dynamic and iterative process, and that adjustments may be necessary to achieve the desired outcome. Stay open to feedback and input from others, and be willing to adapt your approach based on new information or changing circumstances.
10. Cultivating a Creative Mindset
10.1 Embracing Curiosity and Openness
To nurture your creative mindset, it’s important to cultivate a sense of curiosity and openness. Be curious about the world around you, ask questions, and explore new possibilities. Embrace unconventional ideas and different perspectives, and allow yourself to be open to new experiences and insights. Curiosity fuels the creative process and keeps it alive.
10.2 Embracing Failure and Resilience
Failure is an integral part of the creative process. Embrace failure as an opportunity to learn and grow, rather than a roadblock. Understand that not every idea will be successful, and that setbacks are a natural part of the journey. Develop resilience and bounce back from failures with a renewed sense of determination and perseverance.
10.3 Embracing Collaboration and Feedback
Collaboration and feedback are invaluable in nurturing your creative mindset. Seek opportunities to collaborate with others, share your ideas, and learn from their insights. Embrace constructive feedback as a means for growth and improvement. Actively seek out feedback from trusted individuals, and be open to incorporating their suggestions into your work.
10.4 Embracing Continuous Learning and Growth
A creative mindset is rooted in a commitment to continuous learning and growth. Embrace a growth mindset, which believes that abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. Seek out learning opportunities, whether it’s through reading, attending workshops, or taking courses. Be open to expanding your knowledge and skills, and actively pursue personal and professional development.
In conclusion, the creative process is a journey that encompasses various stages, from idea generation to execution. By understanding and embracing each stage, and by cultivating a creative mindset, you can unlock your full potential and unleash your creative genius. Remember that creativity is a skill that can be developed and nurtured, and that setbacks and challenges are a natural part of the process. So, embark on your creative journey with enthusiasm, curiosity, and a willingness to learn and grow. The world is waiting for your unique ideas and contributions.


